Products and Services
Assessment – Design – Implementation

Leachate requires careful treatment; a feature that is often considered as being of a lesser priority in terms of waste management. However, where care is not taken, or discharge consents are not met, the consquences for environmental protection and bottom line profit can be significant. Our products have been proven around the world and are conceived for ensuring optimal environmental protection.
Ammonia Treatment Systems to Comply with Stringent Discharge Consents
If not adequately treated, high levels of nitrate in water can have a significant environmental impact
ammonia
stripping technology
One of the principal contaminants that must be treated in landfill leachate, and in waste water in general, is ammonia. Ammonia-N in normally present in waste water or in leachate in several forms. Treatment is therefore essential.
Visit our website on leachate treatment for more information.
Contaminated Water
Leachate is the liquid that passes through a landfill and is contaminated by interaction of dissolved or suspended elements. Treatment of leachate remains one of landfill engineering’s most complex problems to solve.
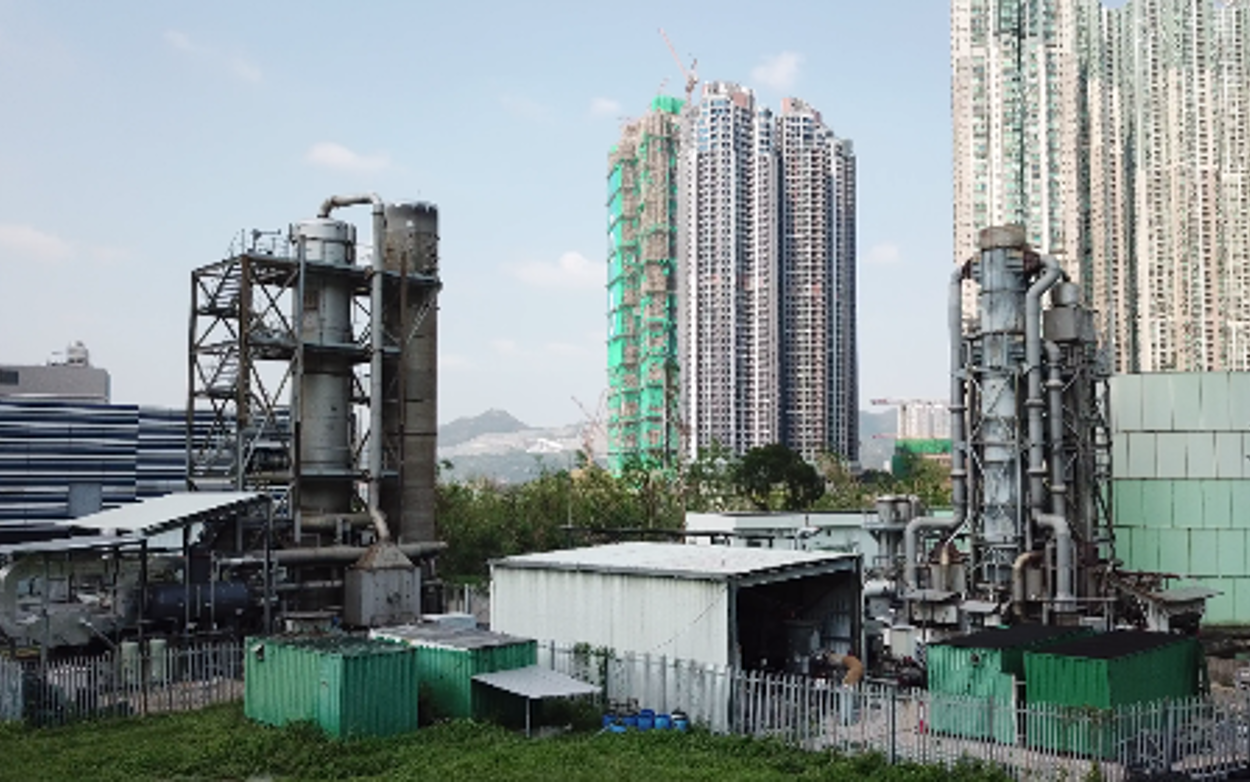
The WENT landfill site in Hong Kong is a major installation serving the city of Hong Kong. The site treats leachate for high levels of ammonia prior to release to the environment. The system uses waste landfill gas to provide a source of heat for the process.

General Information
- Reliable, predictable ammonia removal
- Good for bulk removal of ammonia
- Discharge levels of less than 10 mg/l
- pH adjustment and thermal processes available
- Site specific design-for-purpose
Size Range
Ammonia strippers supplied by Organics can be used for liquid flows of up to 5,000 cubic meters per day. Ammonia reduction of 10:1 can be accomplished with ease. Higher levels of removal may require elevated temperatures, high pH levels or multiple columns. With ammonium ion concentrations of over approximately 1,000 mg/litre it may be necessary to consider some form of exhaust air cleaning, either with an acid wash or by means of incineration.

Key Features
- A low cost method of treating one particular aspect of leachate or other fluids polluted with the ammonium ion.
- This technology will be applicable where the only parameter falling outside of a discharge consent requirement is ammonia.
- Compact plant operating on a physical treatment method and hence more reliable than biological treatment systems.
- Options to instrument the plant for remote monitoring and control.

Typical Applications
Ammonia stripping has its place in the range of techniques applied to landfill leachate treatment where ammonia levels must be reduced but other component concentrations, such as COD and heavy metals, are within the limits of a discharge consent.
The cost of such a system will in general be low compared with other options that may be considered. The power requirement for air circulation is less than that for an equivalent aerated system and water pressure heads required will be a function of the height of the stripper column. When operated with in-line pre-filtration such units can operate for many years with very little maintenance.
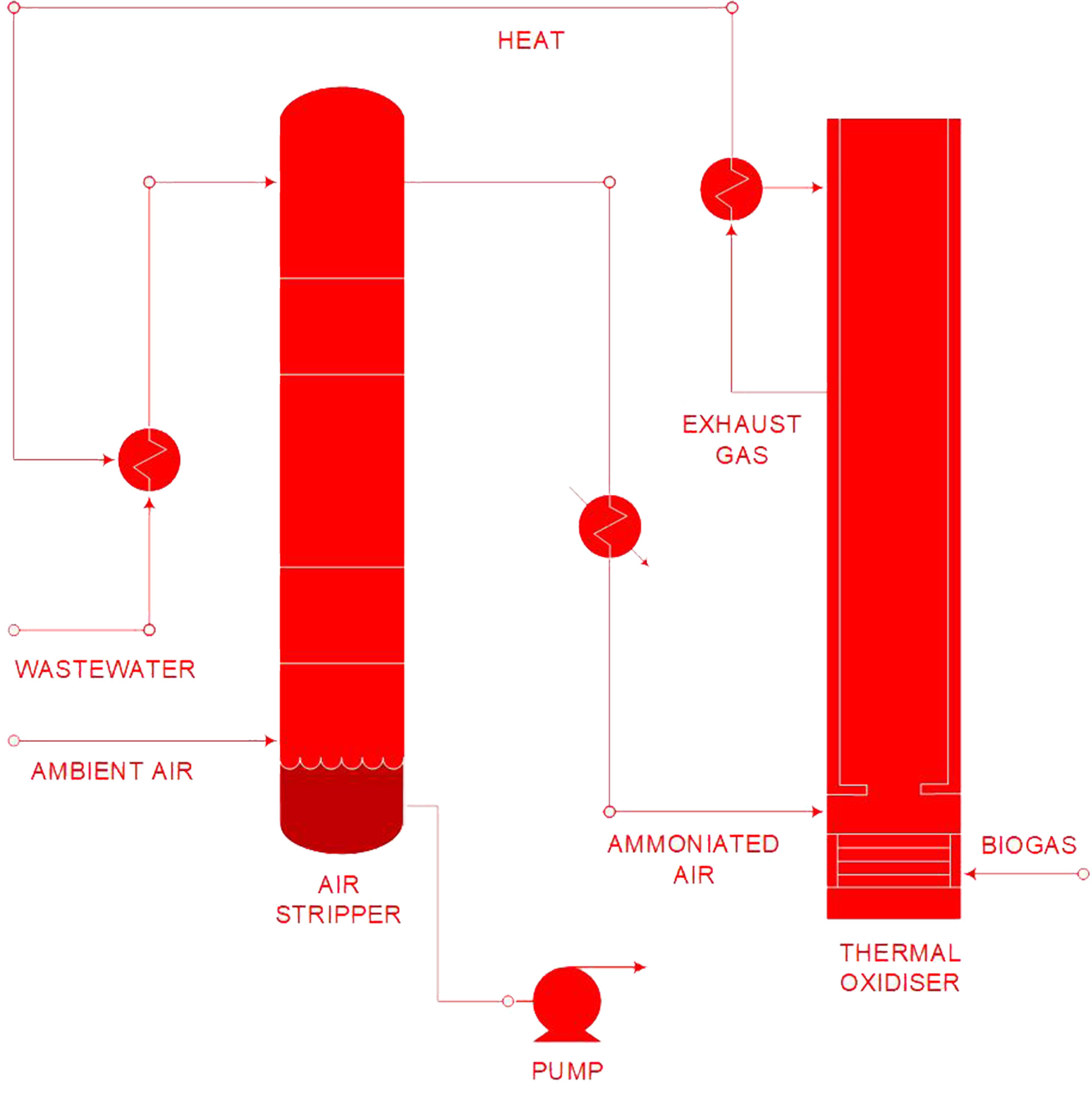
Advanced Thermal Ammonia Stripping
Ammonia Stripping
Thermal stripping provides a low cost alternative to the use of carbon addition in a biological process. The thermal-stripper breaks the ammonium-ion bond with heat alone. This action converts ammonia into a gas, NH3, which can be driven from the liquid-phase with suitable quantities of air. In a single pass it is possible to achieve greater than 98.5% removal of ammonia by this mechanism.
Organics has developed a low-NOx combustion process for flaring waste gas which involves Exhaust Gas Recycle. When combined with the thermal destruction of ammonia gases the result is extremely low NOx emission levels. Heat from the thermal-oxidiser used to destroy ammonia is recovered in conventional heat-recovery economisers and used to power the thermal ammonia stripper.
Ammonia Recovery – Acid Scrubber
The Advanced Thermal Ammonia Stripper with Ammonia Salt recovery has been developed and patented by Organics to provide a fundamental option for disposing of or benefiting from, ammonia removed from wastewater streams. The ATASAS process provides the option of salt recovery by using acid in the scrubber.
Typically, nitric, sulphuric or phosphoric acid may be used to create the ammonium ion salt. In this arrangement, a thermal oxidiser for ammonia-gas destruction is not required. The single important input remains waste-heat with which to drive fracturing of the ammonium ion into ammonia gas.
Heat is required for heating the feed into the ammonia stripper. Such waste heat can be taken from any suitable source, such as a gas engine’s exhaust, excess process steam or any other heat-source where energy is available for disposal. Once the process is commenced, the exothermic reaction encountered in salt formation offers the potential of significant energy savings.
Thermal stripping provides a very low-cost alternative to the use of carbon-source addition in a biological process. The thermal-stripper breaks the ammonium-ion bond with heat alone. This action converts ammonia into a gas, NH3, which can be driven from the liquid-phase with suitable quantities of air. In a single pass, it is possible to achieve greater than 98.5% removal of ammonia by this mechanism.
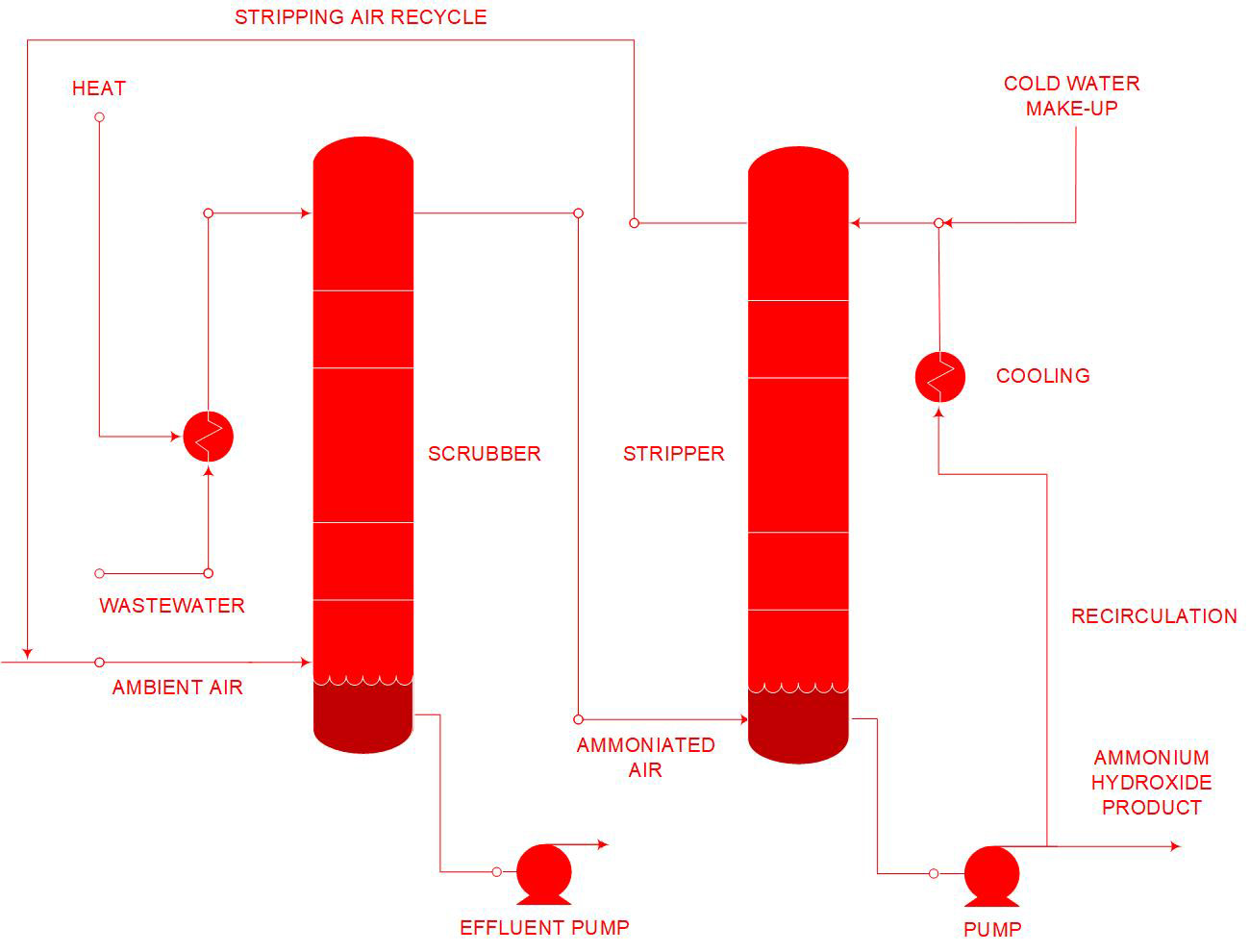
Ammonia Recovery – Water Scrubber
The Advanced Thermal Ammonia Stripper with Ammonia Recovery has been developed and patented by Organics to provide another option for disposing of, or benefiting from, ammonia removed from wastewater streams. The ATASAR process provides the option of either ammonia recovery as an anhydrous liquid under pressure, or as ammonium hydroxide, held in water. The thermal oxidiser is replaced by a cold-water scrubber.
The single important input remains waste heat with which to drive the chemical reactions. Heat is required for both heating the feed into the ammonia stripper, as well as to drive the absorption chiller serving the cold-water scrubber. Such wasteheat can be taken from any suitable source, such as a gas engine’s exhaust, excess process steam or any other heat-source where energy is available for disposal.
Thermal stripping provides a very low-cost alternative to the use of carbon-source addition in a biological process. In many instances, savings can be measured in six digits USD when taken over the lifetime of a project. The thermal-stripper breaks the ammonium-ion bond with heat alone. This action converts ammonia into a gas, NH3, which can be driven from the liquid-phase with suitable quantities of air. In a single pass, it is possible to achieve greater than 98.5% removal of ammonia by this mechanism.
CONTACT US
Ammonia.ie is part of the Organics Group of companies. Please contact us for further details.
ORGANICS GROUP
Please consult the following pages before using our site:
Organics Privacy Policy
Data Privacy and Protection Policy